The world as we know it today, with enterprises heavily relying on cloud services, raises issues that pertain to the need for cloud security enhancing measures even higher. Certified Cloud Security Professional, popularly known as CCSP, is one of the cloud security certifications, suitable for anyone wishing to grow or improve their career in cloud security. This blog post introduces you to the CCSP certification, highlights its importance, discusses how one may prepare for it and such other issues.
How about listening to this article as a podcast?
Understanding the CCSP Certification
What Does CCSP Stand For?
The acronym CCSP stands for Certified Cloud Security Professional. This means that an individual is CCSP-certified and confirmed to have expertise in everything cloud security architecture, governance, management of risk, and compliance. With the transition of businesses to the use of cloud computing services, these pose different responses to security measures and threats. In order to counteract such problems, the CCSP certification encourages and enables professionals to develop the necessary skills and resources to tackle these challenges effectively.
Who Offers the CCSP Certification?
The CCSP certification is provided by (ISC)², an international nonprofit association founded with the sole purpose of advancing the profession of Cybersecurity. (ISC)² offers other notable certifications such as Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP), a certification which many tend to agree is among the best cybersecurity certifications one can ever have.
(ISC)², founded in 1989, has evolved to be one of the most trusted security certification authorities which provides security course programs to professionals interested in information security all over the world. The CCSP certification responds to the needs of specialists who work with cloud computing technology and outlines the difficulties and intricacies involved in securing cloud computing environments.
The Role of (ISC)² in Cloud Security
(ISC)², which is the international information system security certification consortium, helps to formulate, as well evolve, the current standards with regards to the security certification’s architecture. To this end, the organization introduced the CCSP designation to ascertain that individuals who are designated as professional cloud security specialists, have the right understanding, competency and capability to design, build and administrate a secured cloud environment.
CCSP is a certification that is based on a scheme called the Common Body of Knowledge (CBK), which covers essential aspects of cloud security. Such a framework is accomplished through what is called Job Task Analysis (JTA), and updates are made to the framework in documentation every so often in order to ensure that the obtained certification does not become out of practice. In so doing, these high level policies equip the CCSP-certified professionals to handle real-world security issues faced by organizations today.
Eligibility Criteria
To qualify for the CCSP certification, candidates must meet specific eligibility criteria:
- Experience: A minimum of five years of cumulative paid work experience in information technology, with at least three years in information security and one year in cloud security.
- Substitutions: Candidates can substitute a valid Cloud Security Alliance (CSA) Certificate of Cloud Security Knowledge (CCSK) for one year of experience.
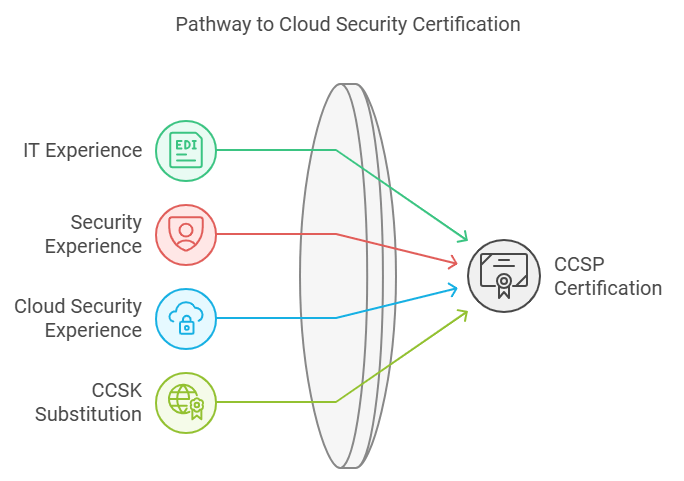
Candidates who may not meet these experience requirements can still pursue the certification by becoming an Associate of (ISC)². This allows them to take the CCSP exam without having all the necessary experience. Upon passing the exam, they will have six years to fulfill the required work experience.
Exam Details
For those professionals who want to obtain the Certified Cloud Security Professional certificate, the CCSP exam is a major milestone. This examination is a measure of your knowledge and dexterity in at least six pertinent cloud security domains, ensuring that you are capable of protecting a cloud environment’s architecture. Therefore, in the sections that follow, we will address each of those domains, their importance, as well as the topics that they cover in brief.
CCSP Exam Structure Overview
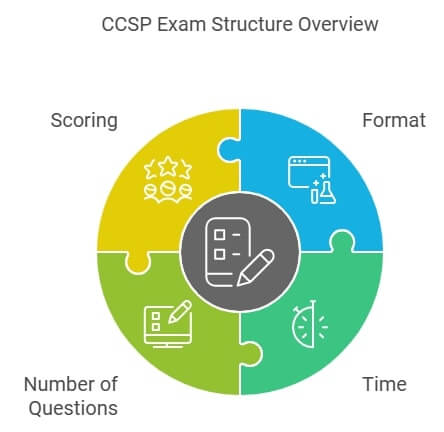
- Format: The CCSP examination is delivered using computer based testing at Pearson VUE test centers or through remote proctoring.
- Time: The examination is to be completed within four hours or less.
- Number of Questions: The examination consists of 150 multiple choice questions inclusive of 100 operational questions and 50 unscored pretest questions.
- Scoring: The minimum pass mark is 700 out of a maximum of 1000 points. The unscored questions are incorporated in the scored questions and hence all questions should be regarded with the same level of seriousness.
Breakdown of CCSP Domains
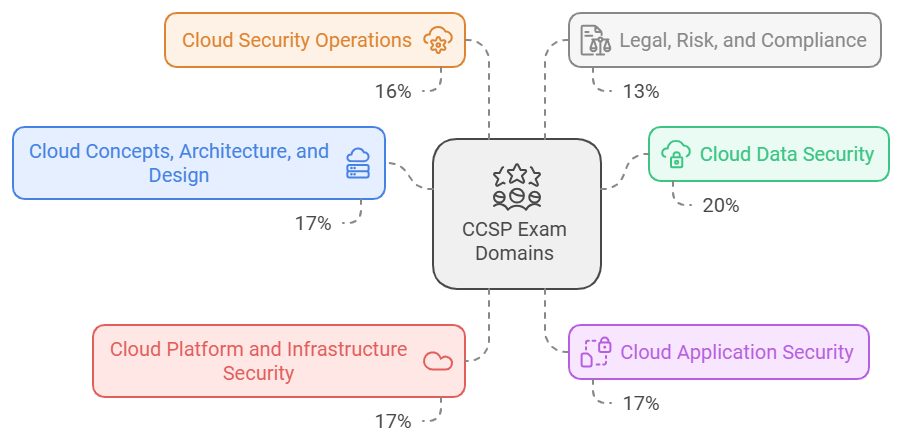
The CCSP exam encompasses six core domains, each representing a critical area of cloud security knowledge. Understanding these domains and their respective weights is crucial for effective study planning. Here’s a detailed look at each domain again in a table format:
| Domain | Weight |
| 1. Cloud Concepts, Architecture, and Design | 17% |
| 2. Cloud Data Security | 20% |
| 3. Cloud Platform and Infrastructure Security | 17% |
| 4. Cloud Application Security | 17% |
| 5. Cloud Security Operations | 16% |
| 6. Legal, Risk, and Compliance | 13% |
Let’s explore each domain in more detail:
1. Cloud Concepts, Architecture, and Design (17%)
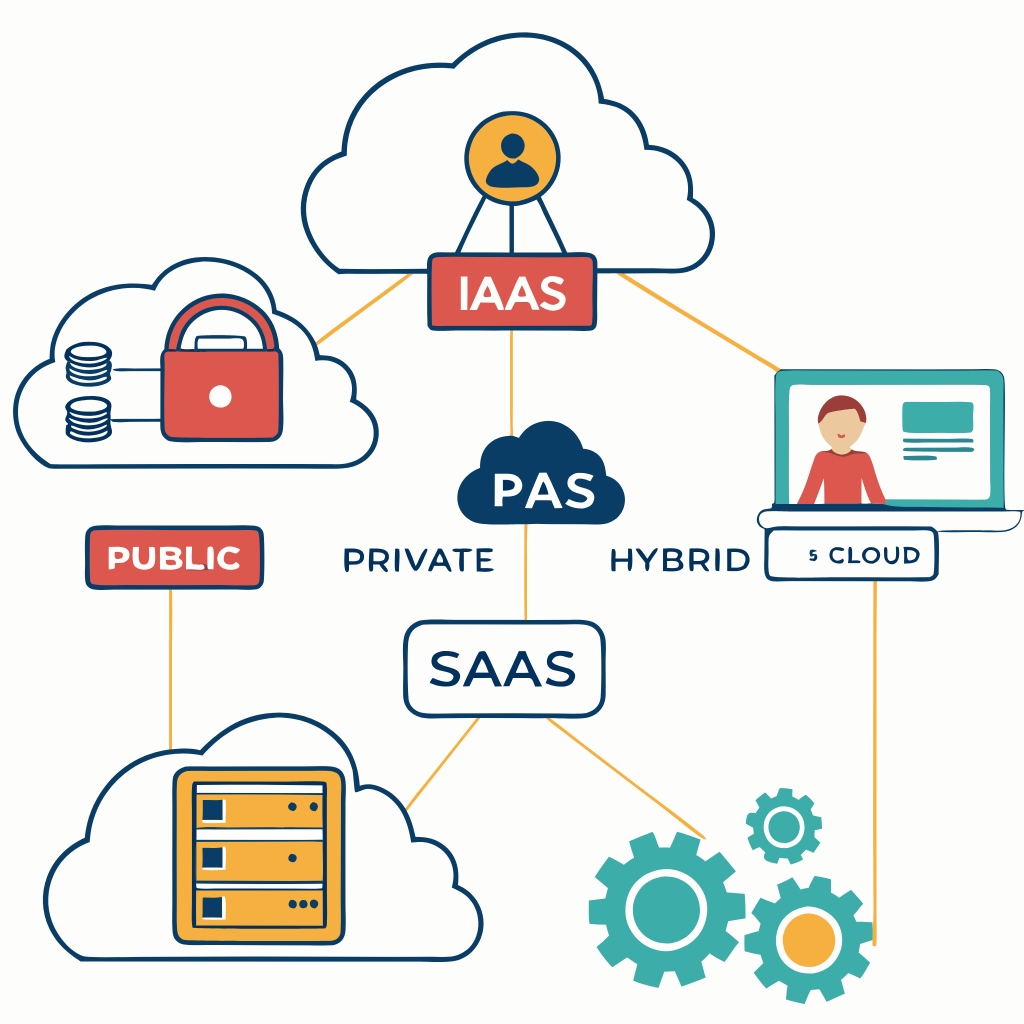
This domain lays the foundational knowledge required for understanding cloud environments. It contains the following topics:
- Cloud Service Models: Define and differentiate the three cloud service models- IaaS, PaaS and SaaS.
- Cloud Deployment Models: Knowledge of cloud structure public, private, hybrid as well as community cloud.
- Shared Security Responsibility Model: The knowledge of how a particular security responsibility is divided between a client and a cloud service provider.
- Secure Cloud Architecture Design Principles: Studying tilting safe clouds design principles in order to reduce risks.
- Cloud Governance Frameworks: Comprehend the existing policies and practices that regulate internal usage of cloud services in an organization.
2. Cloud Data Security (20%)
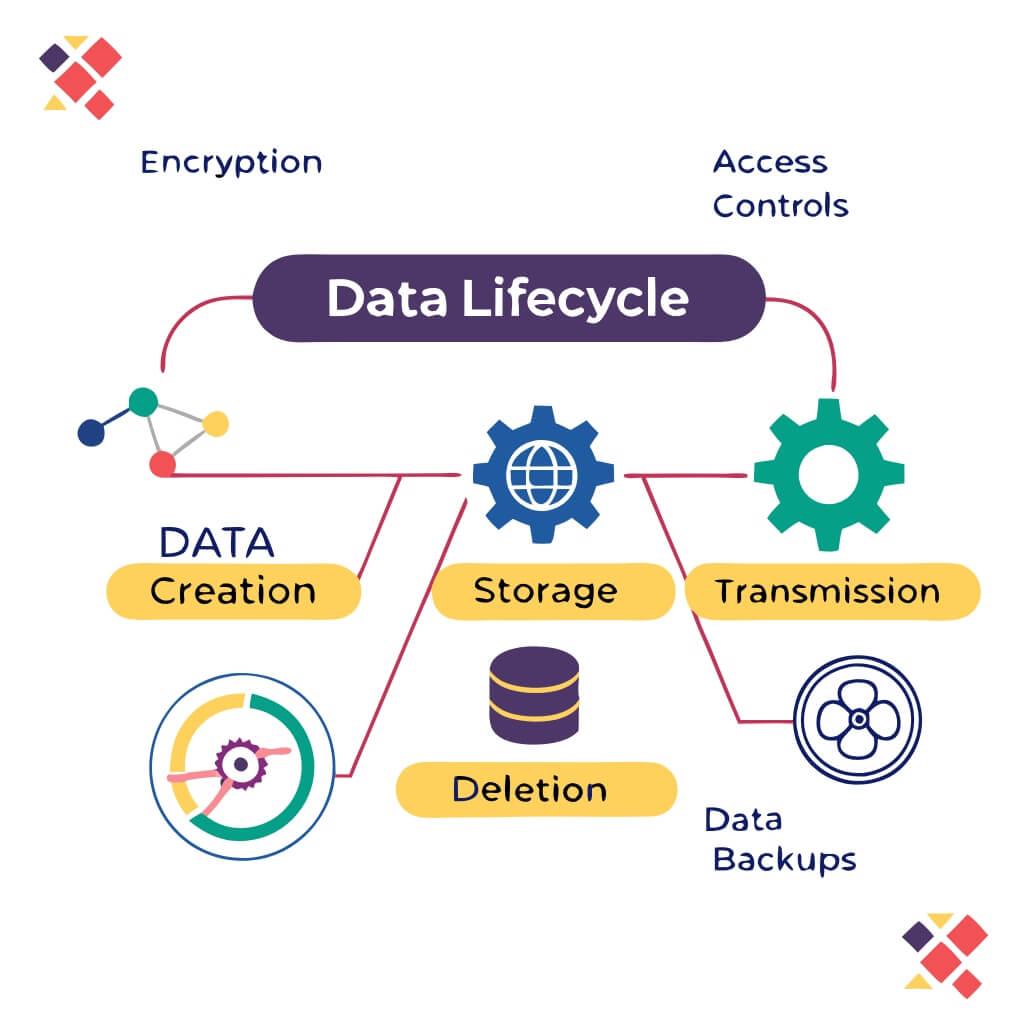
The main focus of this domain is protection of information from cyber criminals in a cloud setting. It involves data encryption techniques, access control mechanisms, and data classification practices. Methods to safeguard data are explored when it is stored somewhere and when it is being sent out. The aim is to deter offensive and hostile actions, such as, access without permissions, breaches, data leaks and sabotage of information. Due to the fact that data is regarded as the most valuable asset of any institution, this domain becomes very important. The topics include:
- Data Encryption Techniques: How to encrypt data at rest and in transit.
- Data Classification and Labeling: How to deal with data in regards to regulation and its level of sensitivity.
- Data Access Controls and Identity Management: Making sure that there are controls in place on who can access the data.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Ways on how to restrict access or spread of the data that is not meant to be leaked.
- Cloud-Based Data Security Solutions: Understanding systems, applications and services that improve data security in the cloud.
3. Cloud Platform and Infrastructure Security (17%)
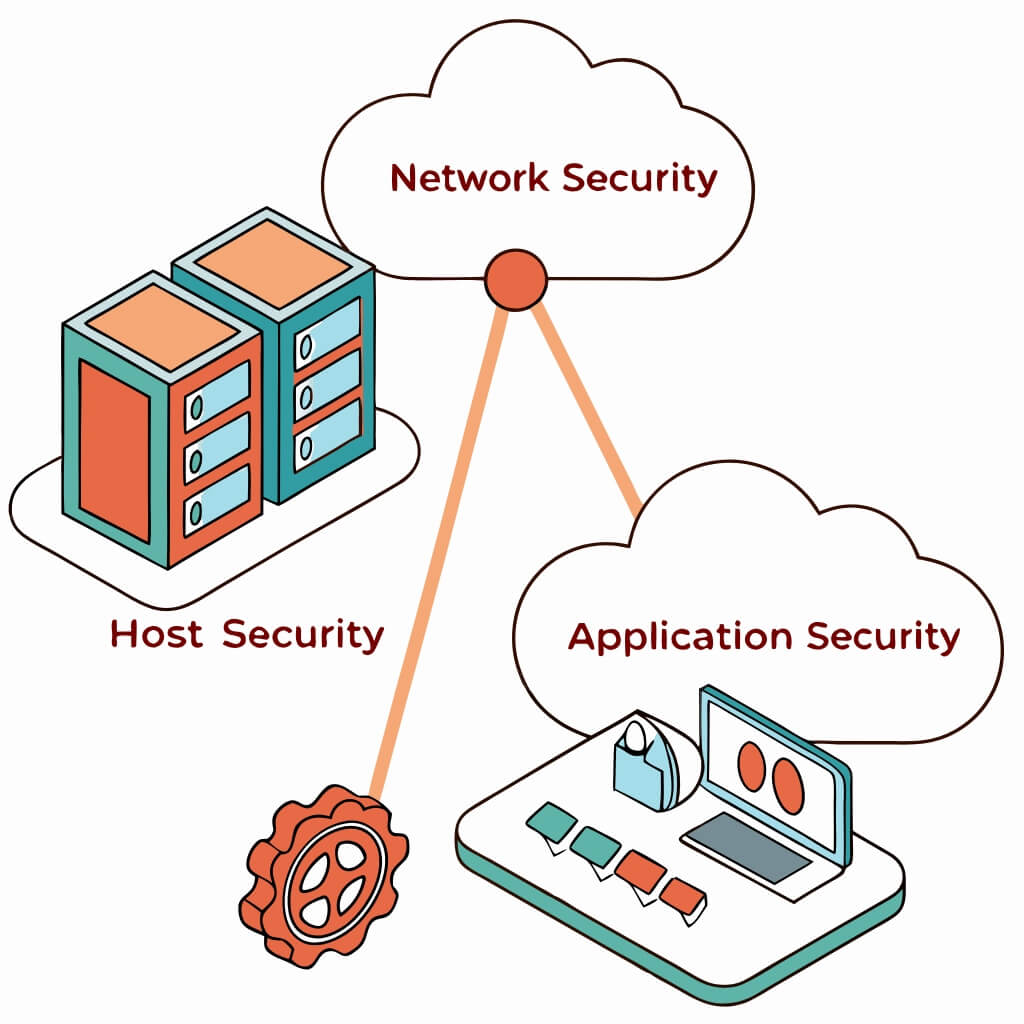
This domain focuses on how to secure the platforms and infrastructure of the cloud. It handles virtualization, defines the network security of the cloud, and gives approaches to how such intrusions can be avoided. Learners study secure cloud application architectures, cloud data security, and identity and access management. They will also study secure cloud network configuration. The main topics are as follows:
- Security of Virtual Machines and Containers – How to secure virtualized environments – working with threats.
- Network Security in Cloud Computing – Such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems within the cloud and their applications.
- Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPPs) – The use of tools that are meant to secure workloads being processed in a cloud environment.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC) Security – Protecting the security of codes written to automate infrastructure.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM)– efficiently controlling people’s access and identities on the cloud services.
4. Cloud Application Security (17%)
This aspect pertains to protecting applications run and/or accessible over the cloud or internet. It includes adherence to software development and coding standards, creation and implementation of system and user authentication techniques, and various encryption techniques as applied to cloud applications. The syllabus aims to provide knowledge on implementing access management policies, secure configurations, application activity monitoring and threat response strategies. In addition, it also discusses the concept of security engineering in the context of cloud application development.
5. Cloud Security Operations (16%)
This domain focuses on the operational maintenance and fending off attacks to an already ‘built’ cloud infrastructure. It includes strategies for the supervision, identification, and handling of security breaches as well as the preparation of emergency response, disaster recovery, and business continuity planning. Students examine interests and behaviors in which information systems include, but are not limited to, secure configuration management, vulnerability assessment, penetration testing, security automation tools, logging, auditing, and network security controls in cloud environments.
6. Legal, Risk, and Compliance (13%)
This domain highlights the importance of understanding legal regulations associated with risk management, and compliance in cloud security. Emphasis is directed to data privacy laws, industry regulations, and international standards.Students learn risk control mechanisms and compliance frameworks, and as a result are able to recognize risks and provide countermeasure plans in response to the risks.
Benefits of Pursuing a Certified Cloud Security Professional Certification
Professional Growth Potential
One can praise the CCSP certification as a cardinal certification which every professional would add in his role. Here are the possible employment positions for CCSP the advanced holders:
- Cloud Architect
- Cloud Engineer
- Cloud Security Consultant
- Information Security Manager
As explained in industry reports, one can expect to earn higher income when in possession of a CCSP certification. Due to the increasing focus on collecting and protecting company’s data, the number of cloud security specialists is on an upward trend.
Credibility and Recognition
Attaining a CCSP certification gives one an additional bearing in the field of cybersecurity. Even better, it shows the effort made towards achieving the highest standards in the industry. When looking for employees to fill \/cloud security positions, companies tend to shortlist candidates who have a CCSP certification.
Getting Ready for the CCSP Examination
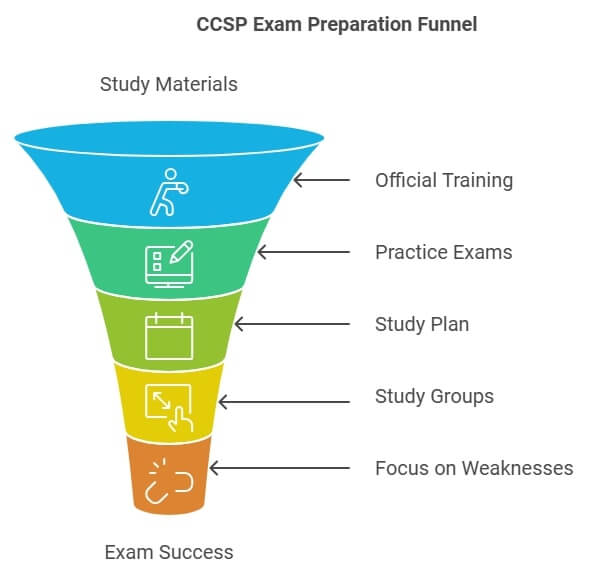
Study Materials and Coursework
Preparation is key to passing the CCSP exam. Here are some recommended resources:
- Official ISC² Training Programs: These are online boot camps and self-paced courses designed specifically to prepare one for the CCSP examination
- Books and Study Guides: Invest into the detailed study guide that addresses all exam domains in full.
- Practice Exams: Take practice examination tests to get used to the examination’s format and kinds of questions that will be asked.
Strategies for Passing the Examination
- Develop a Study Plan: Devote specific periods leading to your examination day for studying.
- Participate in Study Groups: Interaction with fellow students can be encouraging and improve understanding.
- Work on Areas of Weakness: Recognize subjects that you do not feel very strong about and spend more time going through those.
Strategies for Maintaining Your CCSP Certification
- Continuing Professional Education (CPE) Requirements
To maintain your CCSP certification, a minimum requirement of 60 Continuing Professional Education (CPE) credits must be collected within a 3 – year period. This is a way of encouraging you to embrace new practices in cloud security
- Code of Ethics and Professional Conduct
ISC² members and certified professionals are expected to follow a strict Code of Ethics. This includes honor in upholding and advocating the best practices in cyber security.
Comparing CCSP with Other Certifications
CCSP vs. CISSP
Both of these are offered by ISC² certification, but different people use them differently::
- The CISSP certification covers many aspects related to information security in various domains and does not restrict the individual in any way.
- The CCSP certification, however, focuses on cloud specific security practices.
While making the decision, the decision is upon the professional to consider their preferences- whether they want to be all – rounded or a specialist in cloud security.
Other Relevant Certifications
There are several other certifications worth considering:
- Cloud Security Alliance CCSK
- CompTIA Cloud+
- Google Cloud Security Certification
These certifications help build your skillset and make you more marketable for many positions in the field of cybersecurity.
Final Thoughts
To conclude, getting the Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP) certification is a sure way towards acquiring mastery of cloud security concepts. This is an accredited certification that has strict requirements and a detailed course format aimed to improve the chances of earning a living as well as life skills required for modern day technology.