Biometric authentication or biometric security is an up to date technique for establishing one’s identity through the use of distinct physiological characteristics. Given that online security is of utmost importance nowadays, the system works as a better alternative against the use of traditional passwords. Let us get straight into the matter and attempt answering the important question of what is biometric authentication. This will include what it Is, how it works, its different types, and why it is relevant in modern-day society.
How about listening to this article as a podcast?
What is Biometric Authentication?
Biometric authentication is, in other words, the next and probably the greatest step we shall take in order to protect our digital lives. Using physical attributes such as fingers or even the face can go as far as a password and even further. Considering the immense threat to confidentiality and privacy in the modern world, the use of such systems is becoming a necessity rather than an option. Yet still, it is necessary not to forget the significance of this dilemma, apart from its technological significance; we should protect our biometrics from ourselves and handle it responsibly. Revolutions in technologies are likely to change the course of our lives once more, and we won’t be surprised if biometrics goes far beyond just pure security and elevating our digital interactions.
Biometric Authentication Methods
There are a plethora of ways in which biometric technology can help to recognize a person or provide access to a device by one’s gaze through developed computer vision algorithms. They include the following:
Fingerprint Recognition
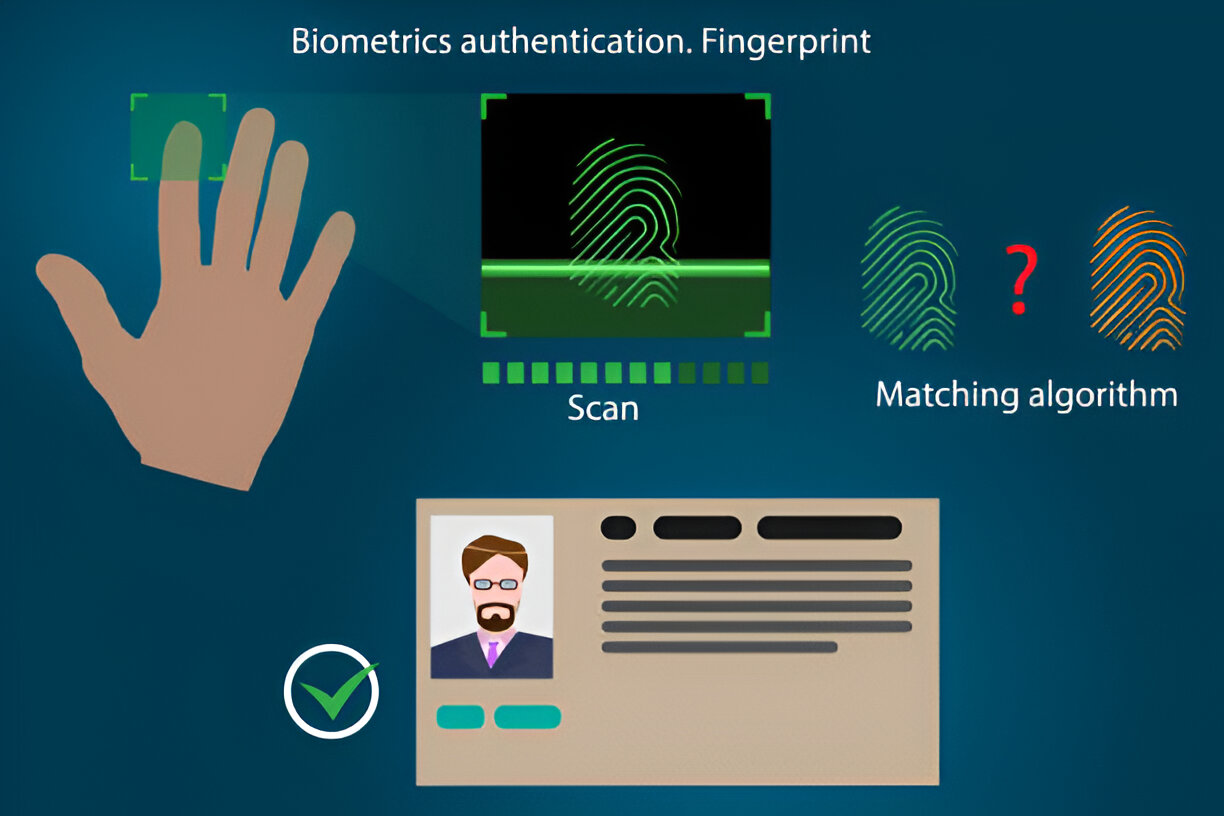
Fingerprint recognition comes together with a thumb impression and is the most widely implemented biometric authentication technique. It works by using specialized imaging to capture ridges and valleys that are unique to individuals at their fingertips. This technique is very popular not only because of its efficiency but also its flexibility.
Iris and Retina Scanning

Iris recognition requires the analysis of the unique designs in the colored part of the eye, while retina scanning looks at the blood vessel patterns in the back of the eye. Both techniques offer high accuracy levels and are hard to forge. Iris patterns belong to only a specific person, hence making this technique most reliable.
Facial Recognition
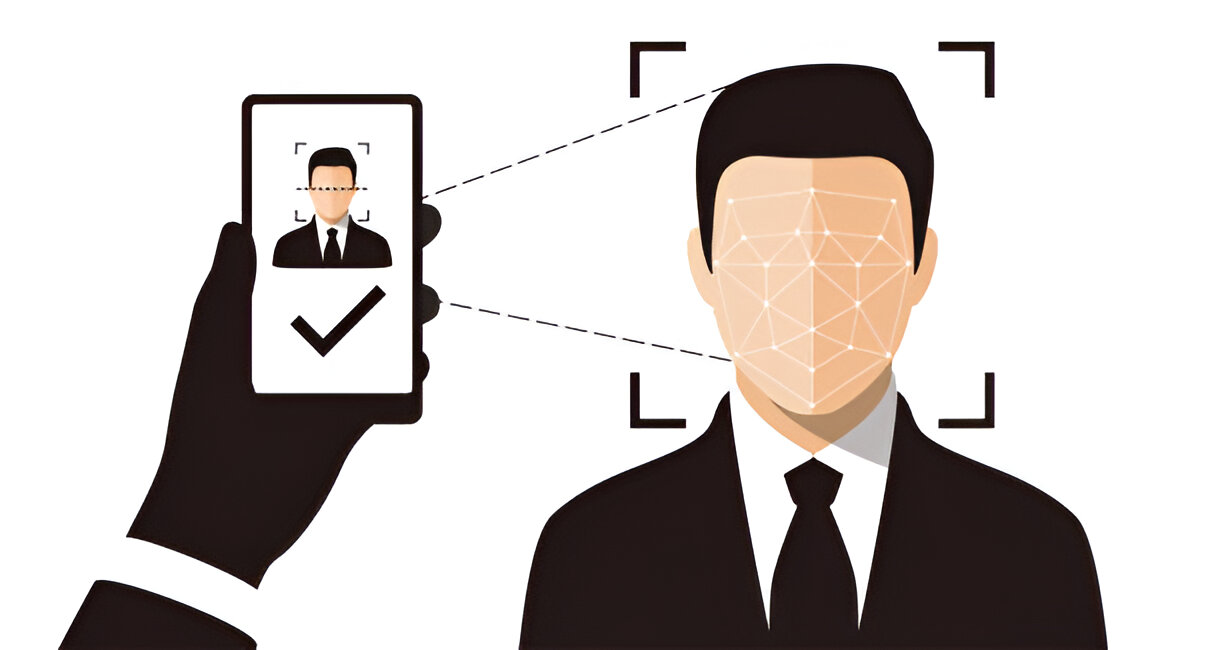
Facial recognition technology works by recognizing different individuals based on some facial characteristics such as inter-eye distance and the nose shape. It is gaining application in both physical security and digital access. It is important to know that facial recognition systems are performance-affected when people change their looks by having facial hairs, wearing glasses or even surgery..
Voice and Speech Recognition

Voice recognition, as the name implies, involves recognizing the voice of a person using trained metrics on their voice properties such as pitch and tone. It can frequently be used on systems and devices for safe entry. Voice recognition systems are also portable, but with certain limitations, they may be viewed as the weakest of all biometric measures because of possible noise intrusion and voice copying.
Summary of Biometric Authentication Methods
| Type | Description | Security Level |
| Fingerprint Recognition | Captures unique fingertip patterns | High |
| Iris Recognition | Scans unique iris patterns | Very High |
| Facial Recognition | Analyses facial features | Moderate to High |
| Voice Recognition | Identifies voice characteristics | Moderate |
The Biometric Authentication Process

Biometrics authentication is a method of cyber-safety based on the detection of human biological characteristics. It consists of the following stages or steps:
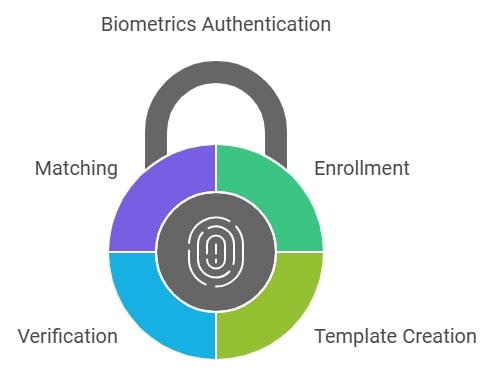
Enrollment and Template Creation Process
- Data Registration: The first stage consists of a person recording their biometric characteristics such as fingerprints, texture of the iris, or structure of the face, etc. This is done using a scanner which encodes the data and saves it as a template for future use.
- Template Creation: The captured data is subjected to a morphological process which generates a digital template that is kept in a database for later comparison.
Verification and Matching
- Scanning: At this point the individual chooses to enter the system and further scans their biometric data. This time the scanning device digitizes the data that is obtained.
- Comparison: This part of the system is called a matcher which is responsible for comparing the newly acquired biometric data with the saved template. If the two data sets are identical, then the system will allow entry. Otherwise, it will not.
Continuous Authentication
- This aspect of the authentication system also permits its continuous use during session, thus allowing the assurance that the said user is the one using the device from the beginning to the end of the transaction. This comes in handy especially where there are sensitive transactions or operations taking place.
To conclude, the process of biometric authentication is built in a way that is both secure and easy to use, which is the reason why it finds a wide range of uses. All the methods have varying levels of accuracy which is important for the dependability of the system. Through the use of these types of characteristics, organizations are able to improve security for the systems but still keep them efficient for users.
Security and Privacy in Biometric Systems
Data Protection, Encryption and Secure Storage Systems
It’s important to protect biometric data because without it, users will not feel safe using such systems. Biometric data protection involves strategies, technologies, and processes that seek to protect biometric data from unauthorized access, theft, or misuse. Whereas passwords come in a form that can conveniently be altered, biometric data cannot. Thus, this data has to be kept in highly sophisticated hashed formats to prevent unauthorized access.
- Biometric data however is mostly rendered in form of templates for ease of storage.
- Such templates are properly encrypted so that no one accesses them without primary authorization.
- In case of breach of such templates, they should not facilitate the reconstruction of the original data.
Spoofing and Presentation Attacks
Biometrics even with their superiority over other forms of identification systems have weaknesses and thus can be counterfeited. Spoofing attacks or presentation attacks happens when the biometric system is fooled by presenting a counterfeit trait. For example, a fingerprint recognition scanner can be spoofed with a finger cast of a lifted print while a facial recognition software can be spoofed with a high-definition picture of a person. In order to address these kinds of threats, many systems these days employ the following.
- Liveness detection which ensures that the biometric trait is from a person who is alive.
- Multi-modal biometrics, the use of more than one biometric data type in order to ensure security.
- Changes to security protocols within specified periods to incorporate new threats.
Ethics and Attitudes towards Privacy
The application of biometric data presents serious ethical issues and privacy concerns. And most people are worried of how their information is been harvested and utilized. To mitigate these issues, organizations should do the following:
- Cultivate openness about the necessitation of collection and how that data will be used.
- Adhere to laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
- When necessary, provide users the ability to exercise control over their personal information.
By focusing on these aspect, companies can create confidence in the users and better use biometrics in activities that do not harm society.
What do you mean by multimodal biometric authentication?
This is a cyber protection technique that allows identifying a person by measuring two or more biological or behavioral traits called identifiers. It is rather like multiple keys being used in unlocking a device. It also falls under the umbrella of Multifactor authentication (MFA) but also does not use the common device entered information MFA. This is where handling many biometric modalities within the same timeframe comes in.
Multimodal biometric authentication has its pros and disadvantages. For one, there is the enhanced security and on the other hand, the elimination of carrying key cards, access cards, users credentials or even pins. This is so because the approach employs multiple unique features making it harder to bypass for the trespassers.
Nevertheless this approach does not come without some disadvantages, For example assembling and putting into practice the materials for the application of multimodal biometrics which include appliances such as scanners and data censors, and storage space for the data, is usually quite costly. Furthermore, the society may consider the process as an overreach in terms of the data collection and storing efforts.
Growing Use Cases Of Biometric Authentication
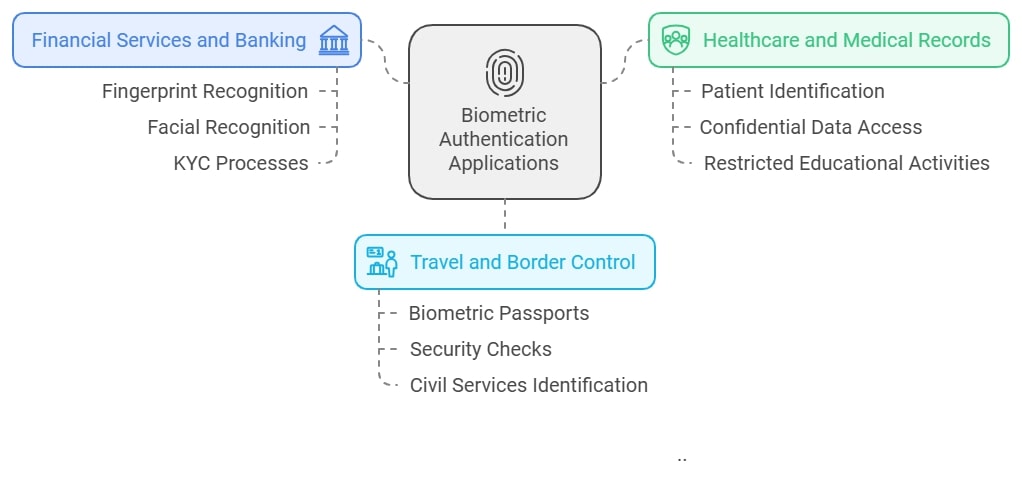
Today, biometric authentication is an integral component of various systems, practical systems included that offer security and comfort in different spheres. There are biometrics as means of identification for almost everything, from unlocking one’s mobile to gaining access to restricted areas. Some important applications include the following:
- Financial Services and Banking
Biometric methods such as fingerprint and facial recognition are employed by banks to secure authentication thereby ensuring that only the account holder is able to access his or her account. These systems are also significant in combating the problem of identity theft in that they verify the identity of the person operating the account. Additionally, during account opening, many banks also employ facial recognition in KYC processes in place of taking pictures of customers.
- Healthcare and Medical Records
Hospitals incorporate biometrics in the identification of patients to minimize instances of misplacing medical records. This system, therefore, allows medical personnel to access confidential data within seconds via a fingerprint or an iris scan, thus improving security and speed. Educational activities regarding certain health programs are also restricted through biometric systems to avoid illegal access to the programs.
- Travel and Border Control
Biometric passports which contain the fingerprint and a facial picture of the individual in question allow for easy border crossings. Also, facial recognition systems are installed in airports to fasten the security checks and boarding. Lastly, the biometrics are also used by the governments to identify the citizens during civil services in a short time.
With advancement in technology, the applications of biometric authentication has been on the rise and this has proved to be a safe and easier way of protecting public as well as sensitive information.
Challenges and Prospective Trends

Technological Constraints and Concurrence
Biometric authentication systems are associated with their own challenges as well. One of the very prevalent challenges relates to the accuracy of biometric systems. Rejection of a user by a system usually not only causes irritation but also breeds mistrust of the system. As a result, developers are trying to enhance the underlying technology of biometric recognition systems. Consider the following aspects – for instance:
- Effectiveness: it is imperative that biometric devices are effective in differentiating and recognizing users.
- Ease of Use: All processes need to be fast and simple for people to accept them.
- Fraudulent Activities: Defenses against counterfeiting and other forms of attacks are most essential.
Legal and Compliance Related Challenges
With the proliferation of biometric systems, there also seems to be an increase in the associated governing frameworks. Most countries have begun consideration of measures which are meant to curb the violation of user rights through the establishment of relevant laws. This is because many individuals are worried about the use of their biological information. Some of the things include but are not limited to the following:
- Data Security: Preventing unauthorized access to or use of such biometric details.
- User Acknowledgment: Guaranteeing that potential users are informed as to the way in which their information will be used.
- Regulations: Adhering to the applicable regimes on a timely basis and avoiding violations of the same.
As has been shown, there are some challenges within biometric authentication systems but there is an opportunity for growth and enhancement. Moving forward is however promising since we will be seeing more intelligent and more accommodating systems than there are today.