Biometric security is a modern cybersecurity technology that uses unique physical traits to confirm a person’s identity. This system is becoming more popular in various fields, from smartphones to airports, due to its precision and ease of use.
In this article, we will cover how biometric security works, its different types, applications, benefits, challenges, and future trends.
What is Biometric Security
Biometric security or biometric authentication is a robust and effective way to confirm who we are, using our unique individual physical or behavioral traits which includes things like fingerprints and facial recognition. This biometric access technology provides a more secure alternative to traditional passwords and keys, making it easier for users to gain quick and secure access to devices and restricted areas without needing complex passwords. Although there are concerns about privacy and security, the benefits of biometric systems are clear. As technology continues to improve, we can expect biometric authentication security to play an even bigger role in keeping our sensitive information safe.
Understanding Biometric Security Systems
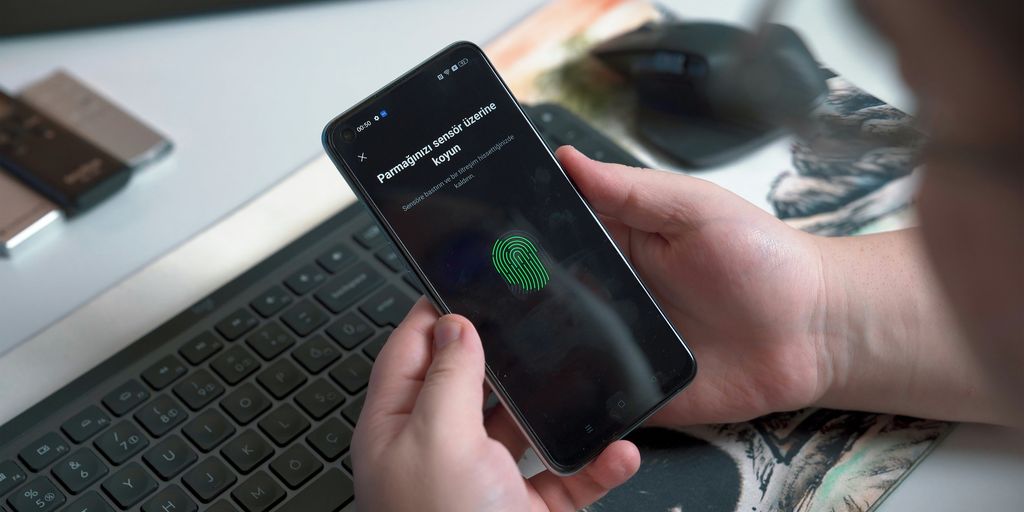

Definition and Key Features
Biometric security systems are advanced technologies that use unique physical traits to confirm a person’s identity. These traits can include fingerprints, facial features, or even iris patterns. This method is highly reliable because it relies on characteristics that are very hard to duplicate.
How Biometric Data is Captured
The process of biometric authentication begins with capturing biometric data through special devices like scanners or cameras. Here’s how it works:
- Data Collection: The system collects biometric ID information.
- Template Creation: This collected data is transformed into a digital template, which is a unique representation of the individual’s traits.
- Storage: The template is securely stored for future use.
The Authentication Process
When someone needs to be verified, the system compares the new biometric sample with the stored template. If they match, access is granted. This biometric access control system is quick and efficient, making it a popular choice for security.
In summary, biometric access control systems provide a modern solution to identity verification, particularly valuable in banking, travel, and device security. They provide a level of security that traditional methods cannot match, ensuring that only the right individuals gain access to sensitive areas or information.
Types of Biometric Security Measures
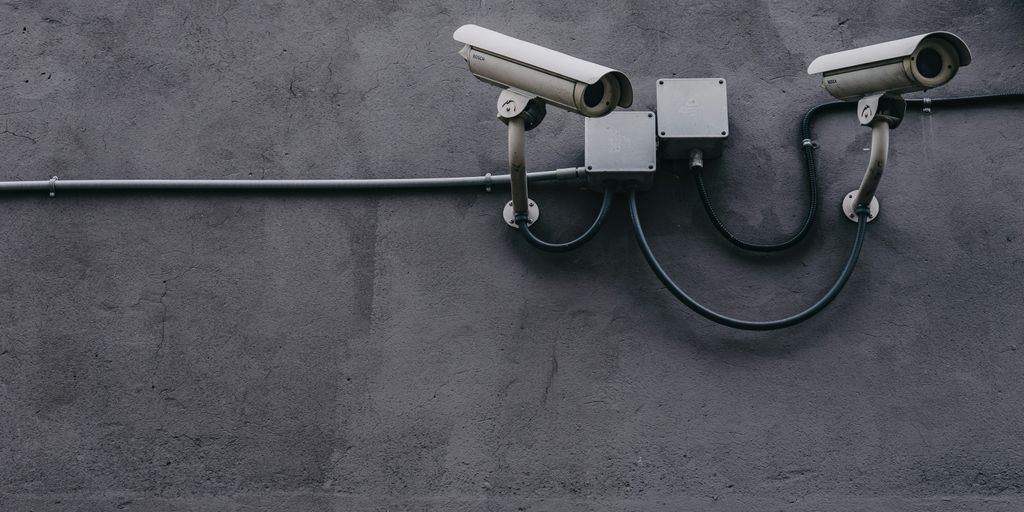

Biometric security measures are innovative technologies that again use unique physical traits to verify a person’s identity. These measures are crucial for enhancing security in various fields. They can be broadly categorised into three main types:
Fingerprint Scanning
Fingerprint scanning is among the most common methods of biometric login for smartphones and security systems. It works by capturing the unique patterns of ridges and valleys on a person’s fingertip for quick and reliable access.
Facial Recognition
Facial recognition technology identifies individuals by analysing facial features. This technology compares a live image to stored templates, making it effective for biometric access in airports and public areas.
Iris and Retina Scans
Iris and retina scans involve capturing the unique patterns in the coloured part of the eye or the blood vessels in the retina. These methods are highly accurate and are often used in high-security environments, such as government buildings.
Voice Recognition
This approach relies on unique vocal characteristics for identity verification, often in customer service or banking, enhancing security and convenience.
Applications of Biometric Security:
Biometric security is transforming how we protect our identities and access secure areas. Its applications are vast across various industries and continues to grow, making it a vital part of modern security systems. The technology is designed to manage the human risks of biometric applications, as it measures intimate body characteristics or behaviours, such as fingerprints, retinas, facial structure, vein patterns, speech, and breathing. Key applications include:
Smartphones and Personal Devices
Biometric login features like fingerprint scanning, facial recognition and even voice recognition secure access to personal devices, making data protection more accessible to users.
Integration in Airports and Border Control
Facial recognition and biometric access control systems speed up immigration and enhance security at borders.
Role in Financial Institutions
Banks incorporate biometric authentication systems such as voice, fingerprint recognition and iris scans for safe and user-friendly mobile banking.
Implementation in Corporate Security
Organizations utilize biometric access control systems for secured entry, employee tracking, and protecting restricted areas.
Pros and Cons of Biometric Security
Benefits of Using Biometric Security
Biometric security offers several significant advantages which include:
- Enhanced Security: Biometric systems provide a higher level of security compared to traditional methods. They rely on unique physical traits, making it extremely difficult for someone to impersonate another person. This means that the risk of identity theft is greatly reduced.
- Convenience: Users find biometric systems easy to use. Instead of remembering complex passwords, they can simply use their fingerprint or face to gain access. This ease of use can lead to quicker access to devices and systems.
- Fraud Prevention: The chances of someone replicating a biometric feature, like a fingerprint, are incredibly low. For instance, the odds of two people having the same fingerprint are about 1 in 64 billion, making it a reliable method for verifying identity.
Potential Risks and Concerns
Despite the benefits, biometric security systems also has some drawbacks:
- Data Security: Biometric data is sensitive and, if hacked, cannot be changed like a password. This makes it crucial for companies to protect this information rigorously.
- Privacy Issues: The collection and storage of biometric ID data raise concerns about privacy. Users may feel uncomfortable knowing that their unique traits are being stored and potentially misused.
- Technical Limitations: External factors can affect biometric scans, this sometimes causes failure to recognise users and lead to frustration.
In essence, while biometric systems offer robust security, understanding their limitations is key to using them responsibly.
Future Trends in Biometric Security
As technology continues to evolve and improve, biometric security is set to become even more advanced. Here are some key trends to watch:
- AI-Enhanced Biometric Systems: Artificial intelligence is set to improve biometric authentication systems by making them even more smarter and accurate.
- Multi-Modal Biometrics: Combining different biometric login methods (like fingerprints and facial recognition) for better security.
- Wearable technology: Devices like smartwatches are starting to include biometric sensors for health and security purposes.
Emerging Applications
- Healthcare: Biometric systems are being used to secure patient records and ensure proper access to sensitive information.
- Smart homes: Home security systems are incorporating biometrics for access control, making homes safer.
- Automotive: Car manufacturers are exploring biometric features to enhance vehicle security and personalisation.
Challenges and Opportunities
- Privacy concerns: As biometric data becomes more widespread, ensuring the protection of personal information is crucial.
- Regulatory compliance: Companies must pay attention to various laws regarding data protection and privacy.
In conclusion, biometric security shows great promise, with potential to revolutionize security across industries while addressing challenges like data privacy and regulatory compliance. With continuous innovation, biometric authentication systems are likely to play a critical role in future security solutions.
Ensuring the Safety of Biometric Data
Data Encryption and Storage
To protect biometric data, it is crucial to use strong encryption methods. This ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable. Here are some key points to consider:
- Encrypt biometric data both in transit and at rest.
- Store data locally on devices rather than on central servers when possible.
- Regularly update encryption protocols to counteract evolving threats.
Compliance with Privacy Regulations
Adhering to privacy laws is essential for maintaining trust. Companies must ensure they comply with regulations such as GDPR or CCPA. This includes:
- Obtaining explicit consent from users before collecting their biometric data.
- Providing users with the right to access and delete their data.
- Regularly auditing practises to ensure compliance.
Addressing Security Vulnerabilities
Biometric systems must be designed with security in mind. Here are some strategies to enhance security:
- Implement multi-factor authentication to add an extra layer of protection.
- Use liveness detection to ensure that the biometric sample is from a real person.
- Regularly update software to fix any security flaws.
The future of biometric data protection relies on integrating privacy considerations into the development and deployment of biometric systems, ensuring they are secure by default. By following these guidelines, organizations can better protect sensitive biometric information from potential threats.



One thought on “What Is Biometric Security and How Does It Work?”